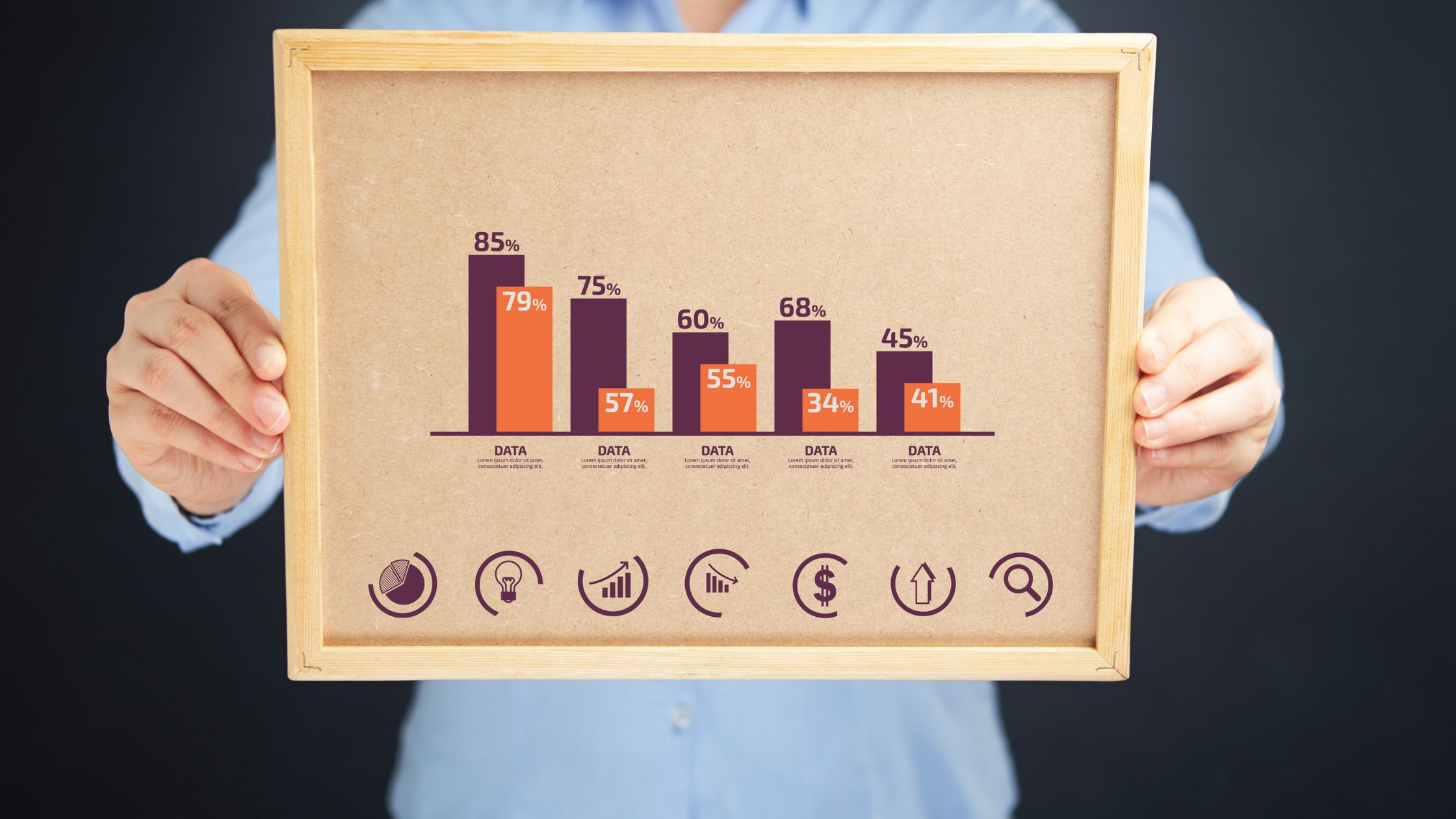
Want to visualize your data in a way that’s both informative and visually appealing? Look no further than the double bar graph! By combining two sets of data side by side, this powerful graphing tool allows you to compare and contrast with ease.
Whether you’re a student, a business owner, or simply someone who craves data-driven freedom, the double bar graph is here to set you free. With its straightforward steps and intuitive design, creating and interpreting double bar graphs has never been simpler.
Benefits of Double Bar Graphs
You can gain valuable insights and make comparisons easily by using double-bar graphs. These graphs are a powerful tool for presenting data in a visually appealing and user-friendly way. By using double-bar graphs, you can effectively communicate information and analyze trends in a manner that’s both clear and concise.
One of the key benefits of Double Bar Graphs is their ability to provide comparisons between two different sets of data. This allows you to easily see the differences and similarities between the two categories being compared. For example, if you’re comparing the sales of two different products over a period of time, a double bar graph can clearly show which product performed better in each time interval.
Another advantage of Double Bar Graphs is that they allow you to display multiple data sets in a single graph. This makes it easier to identify patterns and trends across different variables. By presenting the data in a visually appealing way, double bar graphs enable you to quickly grasp the main findings and draw conclusions.
Steps to Create a Double Bar Graph
To create a double bar graph:
- Gather the data for the two variables you want to compare. This could be anything from survey results to sales data.
- Organize the data into categories or groups that make sense for your comparison. For example, if you’re comparing the sales of two different products, you might group the data by month or by region.
- Decide on the scale for your graph. This will determine the intervals on the y-axis and help you accurately represent the data.
- Once you have all this information, it’s time to actually create the graph. Use graphing software or a tool like Microsoft Excel to input your data and generate the double bar graph.
- Make sure to label the axes and include a title that clearly indicates what the graph is representing.
- Finally, review and analyze the graph to draw meaningful conclusions. Look for patterns, trends, and any significant differences between the two variables. This will help you make informed decisions or communicate your findings to others.
With these steps, you can confidently create a double bar graph that effectively compares two variables.
Creating a Double Bar Graph in Excel
To create a Double Bar Graph in Excel, consider the following steps:
1. Gather Your Data:
- Collect the data you want to represent on your double-bar graph.
- Ensure that your data is organized into two data series and that each data series has its own set of labels.
- Label the columns in your spreadsheet appropriately. One column should represent the x-axis labels, and the other two should represent the data series you want to compare.
2. Create a Scatter Plot Chart:
- Open Microsoft Excel and enter your data into a spreadsheet.
- Highlight the range of cells containing your data, including the labels.
3. Insert a Chart:
- Click on the “Insert” tab in the Excel ribbon.
- In the “Charts” group, click on the “Scatter” chart type.
- Select the “Scatter with Straight Lines and Markers” subtype.
- Your scatter plot chart will be inserted into the worksheet.
4. Adjust the Chart Type:
- Right-click on the chart and select “Change Chart Type” from the context menu.
- In the “Change Chart Type” dialog box, click on the “Bar” chart type and select the “Clustered Bar” subtype.
- Click “OK” to apply the changes.
- Your scatter plot chart will now be converted into a double-bar graph.
5. Format the Chart:
- Click on the chart title and change it to something descriptive.
- Double-click on the x-axis labels and change them to your preferred labels.
- Double-click on the y-axis labels and change them to your preferred labels.
- You can also modify the colors of the bars, add data labels, adjust the gridlines, and make other formatting changes.
6. Add a Legend:
- If your double-bar graph does not have a legend, you can add one by clicking on the “Legend” button in the “Chart Tools” tab.
- The legend will appear on the chart, providing information about the data series.
7. Save Your Chart:
- Once you are satisfied with the appearance of your double bar graph, click on the “Save” button in the “File” tab.
- Choose a suitable filename and location to save the Excel file containing your chart.
Uses of Double Bar Graphs
The uses of double bar graphs include effectively presenting data and analyzing trends, allowing for clear comparisons and identification of patterns. By utilizing this type of graph, you can easily convey information in a visually appealing manner, making it easier for your audience to understand complex data sets.
Here are four key uses of double bar graphs:
- Comparison of two categories: Double bar graphs are ideal for comparing two categories side by side. This allows you to visually represent the relationship between the two variables and easily identify any differences or similarities.
- Tracking changes over time: With a double bar graph, you can track changes in data over time for two different variables. This enables you to analyze trends, identify patterns, and make informed decisions based on the data.
- Highlighting differences: Double bar graphs are effective in highlighting differences between two sets of data. By representing the data in a side-by-side manner, you can easily identify variations and draw conclusions about the significance of those differences.
- Presenting survey results: Double bar graphs are commonly used to present survey results. By organizing the data into categories and displaying them in a visual format, you can easily compare responses and draw insights from the data.
Interpreting Double Bar Graphs
When interpreting double bar graphs, focus on the comparison between the two variables by analyzing the differences in the data displayed. To make sense of the information presented in a double bar graph, consider the following:
- Look for patterns: Examine the bars in the graph and identify any patterns or trends that stand out. Are there any noticeable similarities or differences between the two sets of data? Pay attention to the heights of the bars and their positioning on the graph.
- Compare values: Compare the numerical values represented by the bars. Are there significant differences between the data points? Look for disparities that indicate variations in the variables being measured.
- Analyze the scale: Take note of the scale used on the graph’s axes. Is it a linear scale or a logarithmic scale? Understanding the scale will help you accurately interpret the data and determine the magnitude of the differences between the variables.
- Consider the context: Consider the context in which the data was collected. Are there any external factors that could have influenced the results? Understanding the context will provide valuable insights into the interpretation of the double bar graph.
Tips for Effective Double Bar Graphs
To create effective double bar graphs, utilize an appropriate scale and clearly label the bars to ensure clarity and understanding.
Start by selecting a scale that accurately represents the data you’re presenting. This means choosing intervals that allow for easy comparison between the two sets of data. Avoid using scales that are too large or too small, as this can distort the visual representation of the information.
Additionally, it’s crucial to label the bars clearly. Use descriptive and concise labels that accurately represent the data being displayed. This will help the audience easily identify and understand the information being presented.
Remember to include a clear title for the graph and provide a key or legend if necessary to explain any symbols or colors used in the graph.



